It is a new scientific finding by the DIBIOMEC research group (made up of researchers from the IISPV and the Urology Service of the Joan XXIII Hospital in Tarragona) that could open new avenues for more effective and personalized treatments for this type of patient pacients

Tarragona, September 20, 2024. Prostate cancer (PCa, for its acronym) is the most common among men in Spain (with more than 30,000 new cases diagnosed each year). It is the second leading cause of cancer death in most Western countries. Although it usually develops slowly and in its initial stages it affects only the prostate (causing minimal damage), if it spreads to other parts of the body, such as bones and lymph nodes, it can be fatal. In fact, the number of serious cases is significant. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it early, to make the right choice of treatment and prevent it from getting worse.
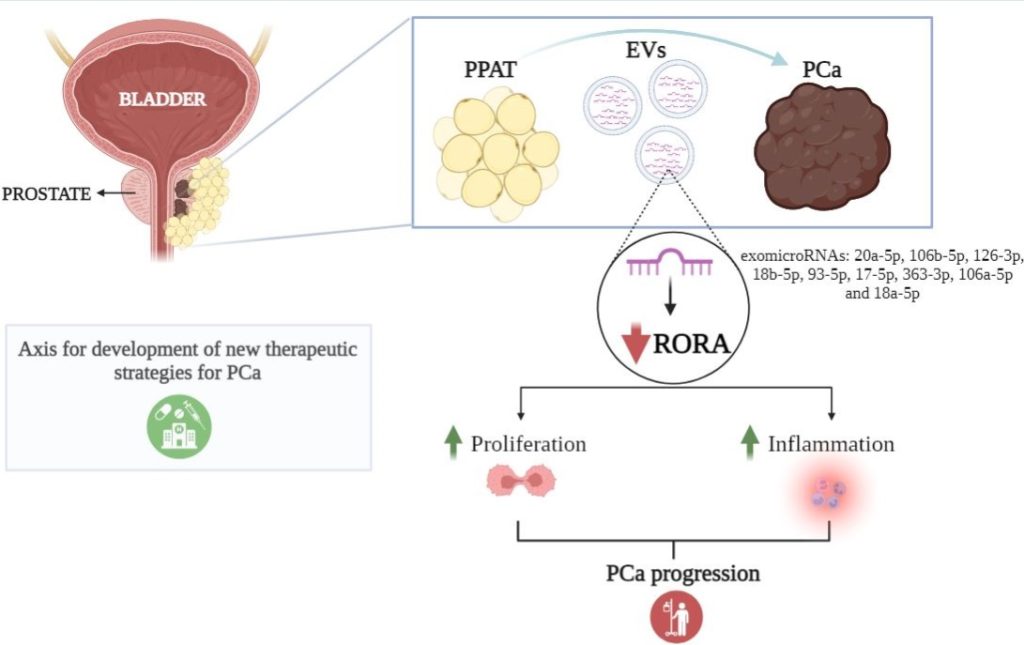
The DIBIOMEC Research Group (Biomarkadores de Enfermedades y Mecanismos Moleculares) of the IISPV and composed of professionals from the Urology Service of the Joan XXIII Hospital in Tarragona, had previously discovered that the periprostatic adipose tissue (also called fat), which surrounds the tumors of prostate, favors the growth of these by providing them with fats so they can develop and proliferate. Recently, these researchers have made another discovery that could represent a new turning point in the approach to the disease: they have identified that this tissue secretes vesicles whose content causes changes in the genes of tumor cells. This contributes to it proliferating and triggering an inflammatory process, enhancing its aggressiveness. Specifically, the molecules responsible for this genetic change in the tumor – according to the study – are known as microRNA, located inside these vesicles secreted by the fat that surrounds it. This discovery offers new strategies for the development of innovative and personalized treatments.
Tumor microenvironment: another important finding
The tumor microenvironment is the cellular environment in which the tumor lives. It includes nearby blood vessels, fat, immune cells, fibroblasts, other cells, signaling molecules and the extracellular matrix. This study also underlines the need to consider the tumor microenvironment when designing new therapeutic strategies since, in the words of Dra. Matilde Rodríguez Chacón, head of the DIBIOMEC Group, “its role is key: it is enhancing the aggressiveness of tumors, and not only in prostate cancer, but in the case of other cancers such as breast cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer… Now it has been seen that the fat that surrounds the different tumors has a very substantial role and should not be overlooked”.
Bibliografic reference: Sánchez-Martin, S., Altuna-Coy, A., Arreaza-Gil, V. et al. Tumoral periprostatic adipose tissue exovesicles-derived miR-20a-5p regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation and inflammation through the RORA gene. J Transl Med 22, 661 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05458-3